All Categories
Featured
Table of Contents
Summer Scorcher Predicted, Again! Double Glazed ... in Canning Vale Perth
Laminated glass is often utilized in areas in the home most prone to injury from human impact such as bathrooms, doors, around staircases and in locations near to the flooring (it satisfies the requirements of 'shatterproof glass' that is mandated for use in these areas by Australian Basic AS 1288 Glass in structures).
Toughened glass has been 'tempered' by being reheated and rapidly cooled once again. This process makes it much more powerful than standard glass it can withstand higher impact loads prior to breaking. It also makes it much safer due to the fact that, when it does shatter, it burglarizes lots of small cubic pieces rather than unsafe shards.
What Is The Best Glazing For My Home? - Part 2 in East Cannington Western Australia
However, toughened glass has no thermal or acoustic advantages over other glass of the exact same toning or density. Secondary glazing is where single-glazed windows are retrofitted with a transparent acrylic or glass sheet connected to the within the frame or openable sash with a secondary frame or with magnetic strips.
![Best Way To Block Sun Heat From Windows [Professionally] in Wembley Downs WA](https://gruenecodesign.com.au/wp-content/uploads/2011/03/windows.jpg)

Secondary glazing will not perform also thermally as a produced IGU, considering that it is difficult to completely seal the perimeter, however it can provide good noise control. Window movies are a thin polymer film containing a soaking up dye or reflective metal layer, with an adhesive backing. They adhere to your glazing to alter its colour or make it reflective.
Glazing in Mullaloo WA
Applied to existing glass, some window films can cut in half the overall SHGC of the window by soaking up and/or reflecting solar radiation. This can be particularly useful in hotter climates where cooling is the main concern, or on east and west elevations straight exposed to extended periods of sunlight. Window films may likewise lower visible light transmittance.
For this factor, it is generally best to use an accredited installer of window film. Frames have a considerable effect on the thermal efficiency of windows and doors, since energy can be acquired and lost through the frame, in addition to through the glass. Different types of frame will permit different levels of heat gain and loss, so cautious option of frame is crucial for efficient passive style.
Why Do You Need Double Glazing Windows In Summer? in Yangebup Western Australia
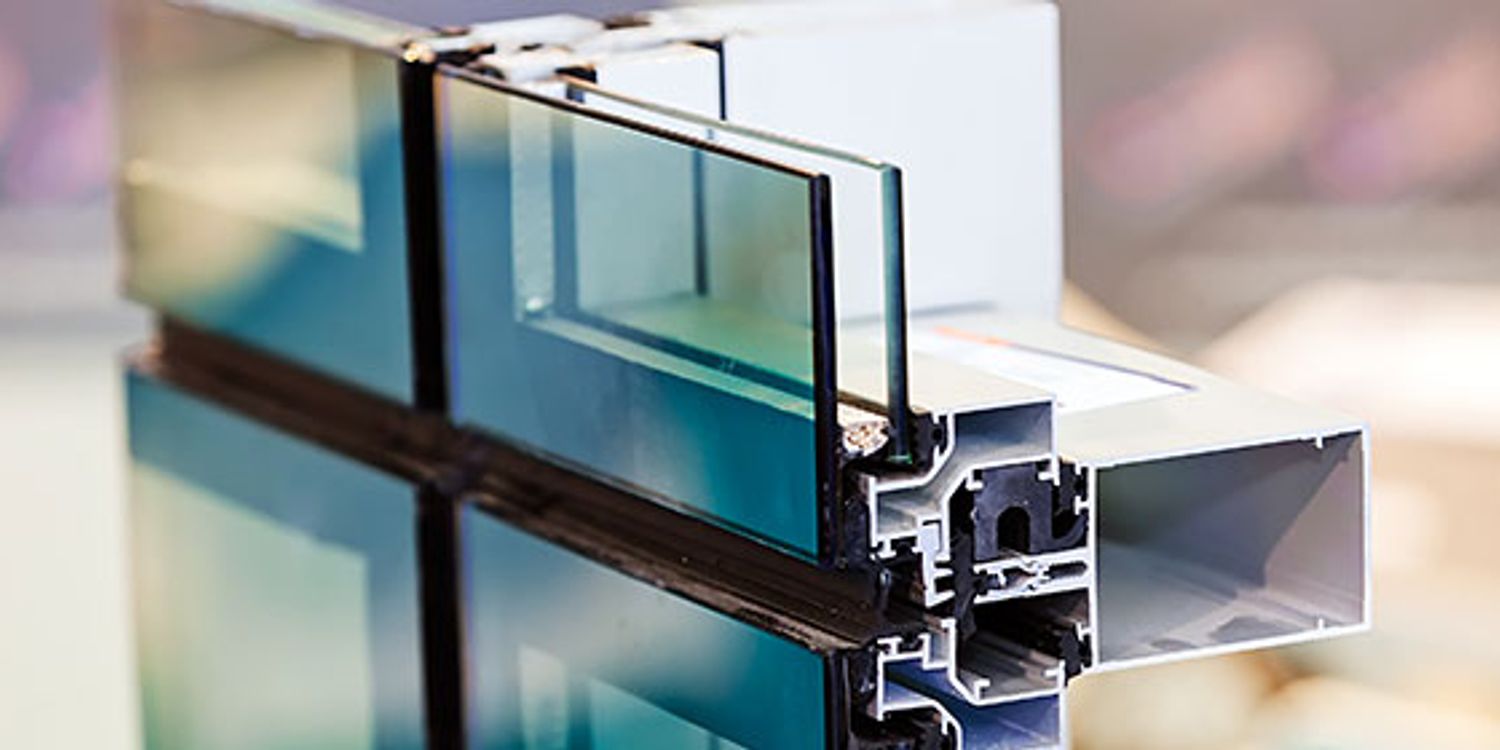
Aluminium is also a really great conductor of heat and will decrease the insulating value of a glazing unit, unless particularly engineered to reduce this. A 'thermally broken' frame is comprised of 2 aluminium sections linked by a structural insulator (generally a low-conductivity structural polymer). This 'breaks' the thermal connection through the aluminium and minimizes the heat flowing through the frame.
Wood frames are an excellent natural insulator that can match some home styles. Lumber frames ought to be made from types that have naturally high sturdiness or be treated to avoid decay and contortion.
Glass Selector - Custom Single & Double Glazed ... in Burswood Western Australia
Nevertheless, this can lead to gaps that allow air infiltration unless good draught sealing (weather removing) is installed. u, PVC is a form of plastic (unplasticised polyvinyl chloride, also referred to as stiff PVC). u, PVC frames provide excellent thermal performance, frequently much better than lumber or thermally broken aluminium. u, PVC is long lasting and needs extremely little upkeep, and can be moulded into intricate profiles that supply outstanding air seals.
u, PVC doors and windows have excellent thermal performance Photo: Ben Wrigley (Light House Architecture and Science) Composite frames use aluminium profiles on the external areas with either a wood or u, PVC inner section. These combine the low upkeep and sturdiness of aluminium with much enhanced thermal efficiency.
Latest Posts
Window Glazing For Households - Energy in Myaree WA
Why You Need Secondary Glazing In The Summer in Madeley WA
Secondary Glazing: Is It Worth It? in Applecross Perth